The advent of blockchain technology has introduced unprecedented opportunities in various sectors, and water utility management is no exception. As global water scarcity becomes an increasingly pressing issue, utilities are exploring innovative approaches to enhance efficiency, accountability, and conservation. Blockchain, with its decentralized and immutable nature, offers a robust solution that can transform how water resources are managed and conserved.
Enhanced Transparency and Accountability

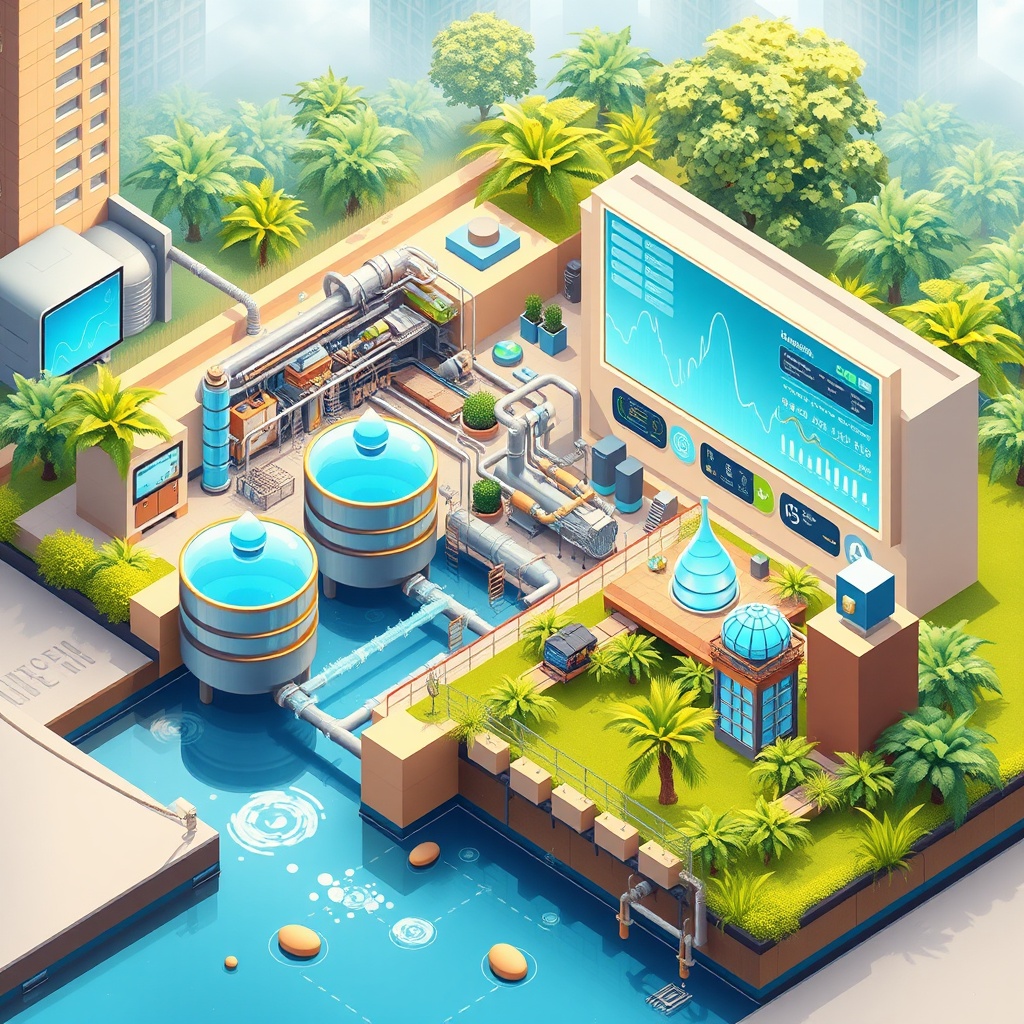
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain in water utility management is its ability to provide enhanced transparency. Traditional systems often suffer from inefficiencies and lack of trust, resulting in poor resource management and wastage. By utilizing blockchain, stakeholders can access real-time data regarding water usage, distribution, and leakages, which fosters accountability across the supply chain.
Smart Contracts for Efficient Operations
Incorporating smart contracts into water utility systems can revolutionize operational efficiencies. These self-executing contracts can automate transactions and processes, ensuring that water delivery and payment occur seamlessly based on predefined conditions. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces operational costs, and enhances the speed of transactions, making water management more efficient.
List of Benefits of Blockchain in Water Utility Management
The following list summarizes the key benefits of implementing blockchain technology in the management of water utilities:
- Improved Data Integrity: Ensures that all data regarding water usage is accurate and tamper-proof.
- Real-time Monitoring: Allows utilities to monitor water supply and demand in real-time, facilitating proactive measures against shortages and leaks.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Customers can track their water usage patterns, leading to better conservation efforts.
- Cost Reduction: Minimizes administrative costs through automated processes and eliminates fraud.
- Decentralized Decision Making: Empowers communities to make informed decisions regarding their water resources.